Drive belts - check and replacement
Examination
1. Turn the crankshaft at the pulley bolt so that the belts can be inspected (or belt) along the entire length. Check for cracks, signs of burning or mechanical damage on the belts. Also check the belt for glossy areas and delamination. If damage or signs of wear are found, replace the belt.
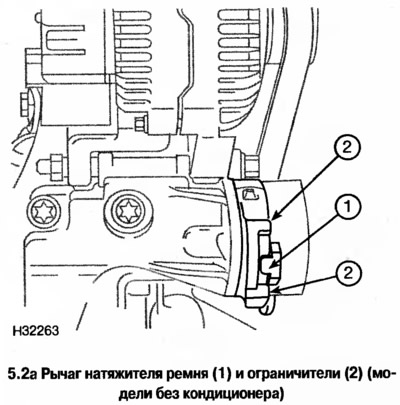
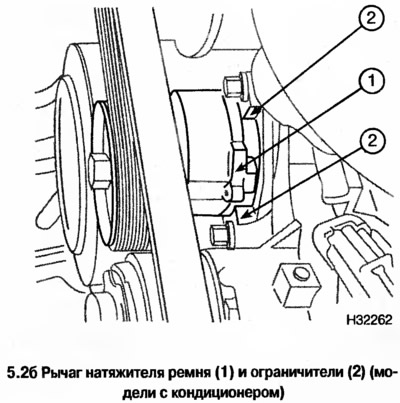
2. Check the position of the belt tensioner lever, which should be located between the stops on the plate (see photo), the lever must move between the stops. If the lever rests against the limiter, then the belt tensioner should be replaced.
Removing
3. Remove the air filter.
4. Remember (or sketch) belt route. Indicate the direction of its movement with an arrow (if the belt does not change).
5. Take the tensioner with a wrench behind the central bolt of the roller and remove the belt.
6. Get a new belt on the pulleys and lay it along the track. Remove the tensioner, bring it to the belt and release it - the belt will tension automatically.
Exhaust emissions test
The check is carried out in a car service. However, if there is no major abnormality in the operation of the engine, and the engine systems health indicator lamp on the instrument panel does not light up, then this check is not necessary.
Checking electrical equipment
1. Check the operation of all instrumentation and electrical equipment.
2. Make sure that the readings of the devices are correct, check the operation of all consumers, including them one by one. Check the condition of the wiring and connectors.
Checking and adjusting the headlights
The check is carried out in a car service.
Checking the condition of the body
Check body and paint condition (on warranty vehicles, the check is carried out in a car service).
Checking the front brakes
1. Remove the wheel and check the remaining thickness of the pads with a ruler through the opening in the front of the caliper.
2. For a more detailed check, the pads should be removed (Chapter 9).
3. Check the status of the disk (Chapter 9).
Checking the rear disc brakes
1. Remove the rear wheels and remove the remaining pad thickness with a ruler through the opening in the rear of the caliper.
2. For a more detailed check, the pads should be removed (Chapter 9).
3. Check the status of the disk (Chapter 9).
Checking the parking brake
The verification procedure is discussed in Chapter 9.
Checking leaks and condition of hoses
1. Inspect all detachable connections of the engine, check for signs of oil or coolant leakage from under the gaskets and seals. Particular attention should be paid to areas near the cylinder head gaskets, cylinder head cover, oil pump and oil pan. It should be borne in mind that very slight leaks from under the gaskets are allowed, which develop over a long period of time, and that only traces of significant leaks are subject to detection. If leaks are found, replace the corresponding gasket or gland, referring to the relevant chapters and sections of the description.
2. Check up also reliability and a condition of fastening of all pipelines and hoses of the engine. Make sure that the wiring is secure, that all clamps, brackets and brackets are present. Breakage or loss of mounting parts leads to chafing of wires and hoses and to serious damage.
3. Carefully check the radiator and heater hoses along their entire length. If blisters, cracks or mechanical damage are found, replace the hoses. Cracks in the hose are best seen when it is bent. Pay special attention to the clamps that secure the hoses to the parts of the cooling system. When the hose is compressed with a clamp, the hose may tear and the development of a coolant leak. Replace all band clamps or cotter pin clamps with worm screw clamps.
4. Check for signs of leakage on all parts of the cooling system (including hoses, connectors and AP).
5. If such traces are found on the parts of the cooling system, replace this part or gasket (Chapter 3).
6. Raise the vehicle and check the condition of the fuel tank and filler neck for dents, cracks or other damage. Especially carefully check the pipe connecting the neck with the fuel tank. Sometimes a leak from the neck or pipe develops due to loose clamps or deterioration of the rubber.
7. Carefully check all rubber hoses and metal tubes connected to the fuel tank. Check for loose connections, damaged tubing, kinked hoses, or other damage. Pay special attention to ventilation tubes and hoses, which often wrap around the neck and are pinched or clogged. Check the condition of the hoses along their entire length, up to the front of the vehicle. Replace damaged sections of pipelines. Check up a condition of all tubes and hoses of a hydrodrive of brakes.
8. On vehicles with automatic transmission, check the condition of the transmission fluid cooler hoses.
Wheel Bolt Check
Remove the caps and check the tightness of the wheel bolts.
Checking the rear suspension lift control pneumatic system (station wagon)
The simplest check of the pneumatic system is considered in Chapter 10. In case of malfunction of the system, contact a car service for repair.
Replacing the heater dust collector
1. On the passenger side, remove the glove box and air duct in the footwell.
2. Replace the dust box (see photo).



Visitor comments