
The heater radiator is connected to the engine cooling system by two hoses running in the engine compartment. The radiator is placed in a plastic casing of the climatic unit, installed under the central part of the instrument panel.
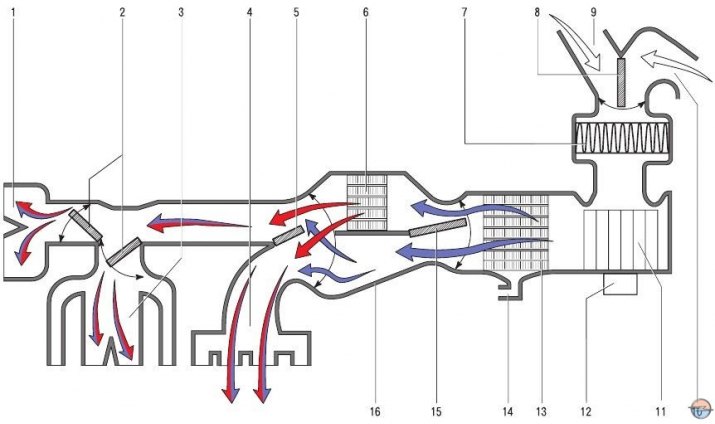
Pic. 1. Schematic diagram of the movement of air flows in the heating, air conditioning and ventilation system: 1 - deflectors blowing the windshield; 2 - dampers for the distribution of air flows to the windshield deflectors and instrument panel deflectors; 3 - instrument panel deflectors; 4 - air ducts for heating the driver's and passengers' legs; 5 - damper for distributing air flows to the instrument panel deflectors and air ducts for heating the driver's and passengers' feet area; 6 - heater radiator; 7 - cabin air filter; 8 - damper of the air recirculation system; 9 - air intake box; 10 - air intake in the car; 11 - fan impeller; 12 - fan motor; 13 - air conditioner evaporator; 14 - drainage hole for draining condensate; 15 - damper of the temperature controller; 16 - housing block of the heating and air conditioning system
The main components of the heater (pic. 1):
- heat exchanger (radiator) 6 heater, designed to heat the air entering the passenger compartment with the heat of the engine cooling liquid;
- fan (blower) 11. Fan motor 12 with permanent magnet excitation, providing a regulated supply of outside air to the heater and air conditioning dampers. To obtain different values of the fan speed, a block of additional resistors is installed in the power supply circuit of the electric motor;
- damper 15 of the air temperature regulator coming from the heater to the passenger compartment. The amount of air passing through the heat exchanger of the heater and the amount of outside air passing through the heat exchanger depends on the change in its position;
- dampers 2 for distributing air from the heater through air ducts to the passenger compartment or for blowing the windshield.

Visitor comments