General information
The rear wheel alignment angles are set at the factory and are not among the parameters under control.
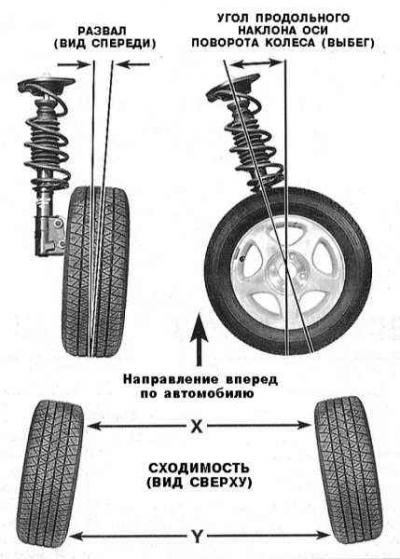
The angles of the front wheels determine the geometry of the position of the latter relative to the suspension of the car and the road surface. Violation of the adjustment of this geometry leads to a decrease in the controllability of the car and an increase in the rate of tire wear. The number of angles of installation of the front wheels of the car to be controlled includes run-out (the angle of the longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation of the wheel), camber, lateral inclination of the wheel axis and convergence Only one of the parameters is subject to adjustment - convergence. Other parameters should be checked on a regular basis to assess the degree of wear of the suspension and steering components.
Vehicle wheel alignment
Adjusting the wheel alignment angles is one of the procedures requiring special measurement accuracy, for the high-quality implementation of which it is necessary to have special, rather bulky and expensive equipment. It would be best to entrust this work to professional car service mechanics. Below, for a general understanding, are the definitions of each of the controlled car wheel alignment angles, the knowledge of which will facilitate the communication of the car owner with the car service personnel.
The angle of the longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation of the wheel (coasting) called the projection onto the vertical longitudinal plane of the car of the angle between the vertical and the axis of rotation of the wheel. If the axis of rotation is tilted back (the lower part of the axle is pushed forward), the runout is called positive, and vice versa. Adjustment of the run-out of the front wheels is carried out by selecting distance washers placed under the push rods of the suspension.
collapse called the angle of inclination of the plane of the wheels relative to the vertical. If the wheels are tilted with their upper edges outward, the camber is called positive, and vice versa. Camber is measured in degrees. The correct camber adjustment determines the size and position of the tread contact patch with the road and allows you to compensate for changes in suspension geometry during cornering and when driving on uneven road surfaces. On the considered models of cars, the possibility of adjusting the camber is not provided.
Tilt angle of the wheel axis called the projection onto the vertical transverse plane of the car of the angle between the vertical and the axis of rotation of the wheel.
Due to the camber and the angle of the transverse inclination of the axis of rotation of the wheel, the points of contact of the wheels with the road are located closer to the axis of the steering knuckle, which supports the so-called «running shoulder» facilitating driving and reducing the effect of transmission of wheel impacts on uneven surfaces to the steering.
Convergence called the amount of convergence to each other of the front edges of the wheels of the car. Such a violation of the parallelism of the wheels allows minimizing tread wear due to skidding when making turns. At zero convergence, the distance between the front edges of the wheels is equal to the distance between their rear edges. Normal convergence usually does not exceed two centimeters. Adjustment of the convergence of the front wheels is carried out by adjusting the length of the steering rods by changing the position of their tips. To adjust the toe-in of the rear wheels, a special adjustment cam bolt is provided, screwed into the inner end of the rear suspension control arm. Violation of the adjustment of convergence leads to accelerated wear of the tire tread due to their slippage on the road surface.
Conditions for checking wheel alignment
1. Checking the installation angles of the car requires a viewing hole or a special measuring lift. When performing a measurement, the following conditions must be met:
- The air pressure in the tires meets the requirements of the Specifications in the Chapter Suspension and steering;
- The front wheels are set in a straight position;
- The car is not loaded, the fuel tank is full;
- The suspension of the car is strongly compressed;
- The steering gear is correctly adjusted;
- The backlash of the articulation of the suspension and steering components does not go beyond the permissible ranges;
- The tread depth of tires of one axle is the same.
2. All parameters, except for convergence, are set during the production of the car and are not subject to adjustment. Unless the vehicle has been in a serious accident, wheel alignment must be maintained throughout the life of the vehicle. In the absence of confidence in the correctness of the definition of parameters not subject to adjustment, seek help from specialists.
3. At home, convergence can be measured in two ways. In the first, the distances between the front inner edges of the wheel rims are measured with a suitable meter. The second method will require a special plate. By setting the plate perpendicular to the wheel and rotating it, wheel deflection can be detected. A meter or plate can be purchased from specialized stores.
4. If as a result of the check it turned out that the convergence needs adjustment, loosen the lock nuts of the tips Turn the steering wheel all the way to the left and accurately count the visible number of threads on the right steering rod. After that, turn the steering wheel all the way to the right and count the visible number of threads on the left pull. If the two numbers match, subsequent adjustments will require both lugs to be unscrewed or screwed in by the same number of turns. If the results obtained differ from each other, the subsequent adjustment must compensate for the difference. After adjustment, both rods must have the same number of loose threads.
5. Having finished the adjustment, tighten the locknuts - since the rods rotated, the protective covers of the steering mechanism will most likely be deformed and the collars of their fastening should be loosened and the appropriate corrections should be made.
Adjustment of a convergence of forward wheels
1. Set wheels to straight ahead.
2. The exact position is determined by reaching the control dimension (1).
Setting the wheels in a straight-ahead position
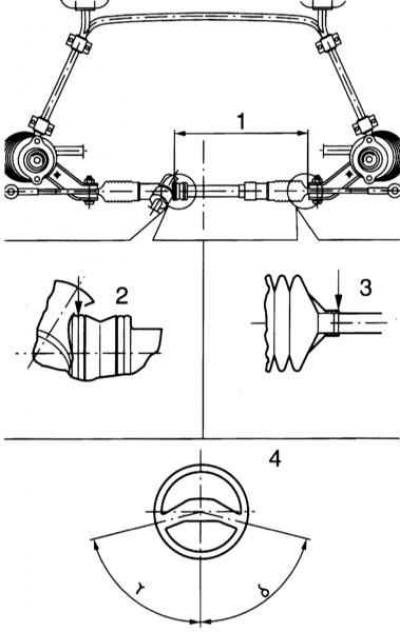
1 - Control dimension:
Models without power steering 420±2 mm
Models with power steering 435±2 mm
2 — the Left ledge of a case of the steering mechanism
3 - Ledge for protective cover
4 — the Central position of a steering wheel
3. Install the OPEL KM-551-2 control template between the left ledge of the steering gear housing (2) and right ledge for the protective cover (3).
4. In this position, the steering wheel should be straight (4). If there is a deviation from the central position by an angle of more than±5 degrees, remove the steering wheel and install it directly on the steering shaft.
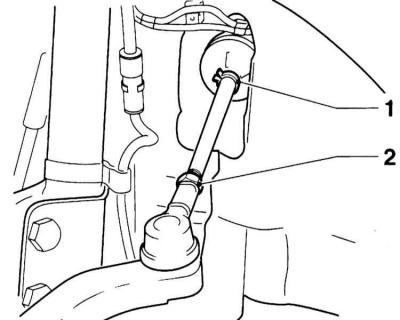
5. Remove the clamp (1) securing the protective cover and give the locknut (2) tie rod end.
clamp (1) protective cover and tie rod end locknut
6. Adjust toe-in by turning both tie rods.
In this case, it is necessary to maintain the length of the steering rods.
Length (1) tie rod end
7. Tighten the tie rod end locknut to 50 Nm.
8. Adjust the protective cover and secure it with a clamp.
9. Check the front wheel toe-in adjustment again.

Visitor comments