Remember that the dust generated during the operation of the brake mechanisms may contain asbestos, which is extremely harmful to human health. Never blow off dust with compressed air or inhale it; when servicing mechanisms, wear a protective mask or respirator. Never use gasoline or petroleum-based solvents to clean brake system components - use only branded cleaners or methyl alcohol!
More detailed illustrative material on brake mechanisms is given in Chapter Brake system.
The condition of the brake system components, in addition to the regular checks specified in the routine maintenance schedule, should be assessed each time the wheels are removed or if signs of a malfunction of the brake system appear.
The following symptoms may indicate a malfunctioning brake component:
- When braking, the car loses directional stability (pulling to one side);
- During braking, the brake mechanisms emit a screech or creak;
- Excessive travel of the foot brake pedal;
- When depressing the brake pedal, pulsations are felt;
- There are signs of a brake fluid leak (usually on the inner surface of wheel rims and tires).
1. Loosen the wheel nuts.
2. Jack up the car and put it on stands.
3. Remove wheels.
Disc brakes
The caliper of each of the brake mechanisms is equipped with two pads (internal and external). The ends of the pads are clearly visible through a special viewing window in the caliper body after removing the wheel.
Thickness of brake pad with base
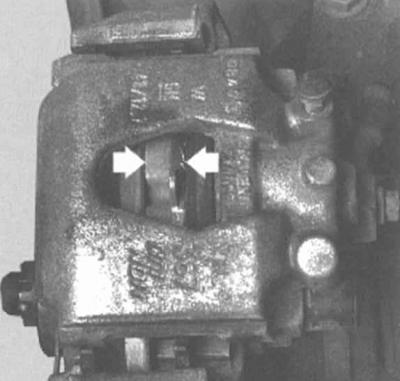
Evaluation of the residual thickness of the friction lining of the inner pad is made visually through the viewing window of the caliper. If the pads are worn beyond the allowable limit (see Vehicle settings and routine maintenance), it is necessary to make a complex replacement of the brake pads.
1. If it is difficult to visually assess the residual thickness of the pads, or there is a need for a more detailed inspection of the pads, remove the caliper (s) and remove the pads for a more detailed study (see chapter Brake system).
2. After the pads are removed from the caliper, clean them with a special tool and check the residual thickness of the pads with a ruler or a vernier caliper equipped with a vernier.
3. Measure the thickness of the brake discs with a micrometer. Compare measurement results with regulatory requirements (see Vehicle settings and routine maintenance). If the thickness of any of the discs is out of range, replace it (see chapter Brake system). If the thickness of the disc is normal, check its general condition. Pay attention to defects such as deep scratches, grooves, scuff marks, overheating marks, etc., if necessary, remove the disc and give it to the groove (see chapter Brake system).
4. Before replacing the wheels, inspect all brake lines for signs of damage, wear, deterioration due to aging of the material, signs of leakage, bends, twists and other deformations (in particular near the points of connection of flexible brake hoses to brake calipers. Check up reliability of fastening of hoses collars. Make sure that none of the brake hoses come into contact with sharp corners of adjacent bodywork, exhaust system components and suspension (at any position of the steering wheel). If necessary, make appropriate repairs or correct the route of laying the lines. Replace defective components (see chapter Brake system).
Drum brakes
1. When checking the rear drum brakes, make sure the parking brake is released, then tap the outside of the drum with a soft-faced hammer to loosen the fit.
2. Remove the rubber cap of the inspection hole on the rear brake shields and shine a flashlight into the hole. Check the thickness of the pads. The wear limit has been reached if the lining has a thickness 2.5mm (without metal backing).
Hole for assessing the thickness of brake adjustments
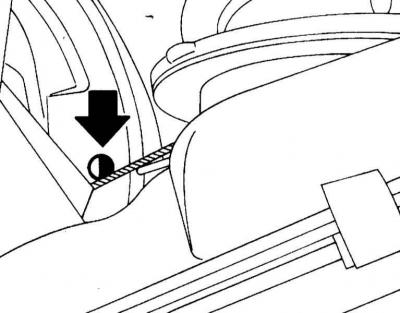
Never blow brake dust off the surface of components with compressed air or inhale it - the dust may contain hazardous asbestos!
3. If necessary, make a complex replacement of the shoes. The shoes must also be replaced if cracks are found, areas of the linings polished to a shine, or traces of brake fluid ingress.
It is necessary to replace the brake pads of the entire axle.
4. Make sure that all the springs of the brake mechanism assembly are properly connected and in good condition (see chapter Brake system).
5. Check assembly components for signs of brake fluid leaks. Using a finger or small screwdriver, carefully pry the rubber boots off the wheel cylinder at the top of the shoes. Identification of any signs of leaks in these areas requires an immediate reconditioning of the cylinder assembly (see chapter Brake system). Also check all brake hoses and their fittings for signs of leaks.
Check wheel cylinder for signs of brake fluid leaks

6. Thoroughly wipe the inside of the drum with a clean cloth soaked in methanol. Avoid inhaling dust containing asbestos.
7. Inspect the drum surface for cracks, nicks, overheating, or other damage. If defects cannot be removed by surface treatment with fine-grained sandpaper, the drum should be given to a car service workshop for turning.
8. Repeat the procedure for the opposite brake components. Reinstall the drums, secure the wheels and lower the vehicle to the ground.
Vacuum booster
Check of serviceability of functioning of the vacuum amplifier of brakes is made from a driver's seat.
1. With the foot brake pedal fully depressed, start the engine - the pedal should fall a little more.
2. With the engine running, depress the foot brake pedal several times. The amount of pedal travel must remain constant.
3. Depress the pedal, turn off the engine and continue to hold the pedal down for about 30 seconds more, during which it should not fall down or rise.
4. Start the engine again, let it run for a minute, then shut it off again. Again, firmly depress the pedal several times - the amount of travel should decrease with each stroke.
5. In the event of a negative result of the described test, the brake booster servo must be replaced (see chapter Brake system).
Parking brake
The parking brake is controlled by a lever located between the front seats. After pulling the lever, cock it to the stop, while counting the number of clicks of the ratchet mechanism. If the number of clicks is out of range (see Vehicle settings and routine maintenance), the parking brake actuator is subject to adjustment (see chapter Brake system).
Alternatively, the parking brake can be checked for proper operation by parking the vehicle on a downhill section of road and immobilizing the parking brake with the transmission in neutral. If the brake does not hold the vehicle when cocking its lever to the required number of clicks, it is necessary to make an adjustment (see chapter Brake system).
Pressure control valve in the hydraulic circuits of the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels
Since there are two diagonal brake circuits, two pressure regulating valves are required. The valve-regulator provides a slower increase in the pressure of the brake fluid going to the rear brakes than the brake fluid going to the front brakes. Thus, excessive braking force of the rear wheels is eliminated and the stability of the vehicle during braking is increased.
The decelerating brake force regulator is installed at the bottom of the vehicle above the rear suspension and is controlled through the rear suspension spring. Before checking the regulator operation, check the brake fluid pressure to the front and rear brakes. Valves-regulators are replaced only in pairs. The designation of the installation side of the regulator is stamped on its body.
Location of control valves
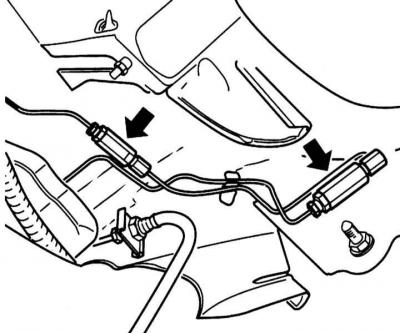
Checking the serviceability and adjusting the pressure regulator valve is carried out on an unloaded and standing on wheels car (fuel tank half full).
Functional check
1. Have an assistant observe the pressure control valve. Firmly depress the brake pedal and release it quickly.
2. With this lever (1) valve-regulator should move If the lever does not move, replace the regulator by contacting a service station for help.
Control Valve Control Components
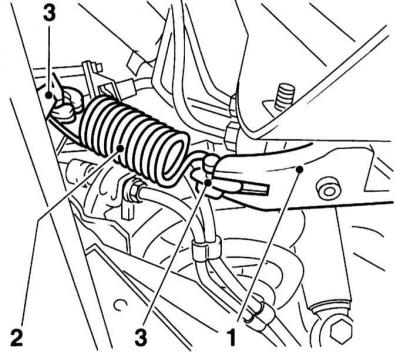
1 - Lever
2 - Coupling spring
3 - Supports
Adjustment
1. Press the lever (1) in the direction of vehicle travel until it stops. Return spring (2) must lie in plastic supports (3) without gap and tension (refer to illustration).
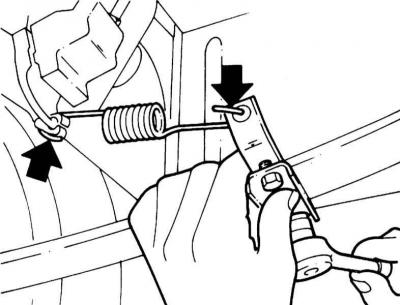
2. On models Hatchback to adjust, loosen the adjusting bolt and move it so that the spring fits without play or tension.
Loose adjusting bolt
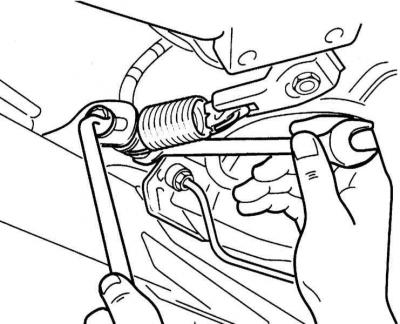
3. On models Combo to adjust, loosen the spring holder and move it so that the spring fits without play or tension.
Holder loosening
4. Tighten the fastening bolt with force 20 Nm.

Visitor comments