Some special maintenance procedures that require additional fluid level checks are also described below. Check under the vehicle regularly for signs of fluid leaks.
The compilers of this Guide recommend checking the levels of the main working fluids (engine oil, coolant, windshield washer fluid, battery electrolyte, power steering fluid) on a regular basis, at least every 7500 km. The rest - in accordance with the maintenance schedule (see Section Schedule of ongoing maintenance).
Various fluids play the role of working fluids in lubrication, cooling, braking, clutch, heating and air conditioning systems, glass washing, etc. Due to the fact that all fluids are subject to thinning and exhaustion over time, and also gradually become contaminated during the normal operation of systems, it is necessary to periodically replace them completely. Please refer to the list of fluids recommended for use in your vehicle before attempting any level adjustment or replacement (see Specifications to Chapter Vehicle settings and routine maintenance).
When checking fluid levels, the car must be parked on a flat horizontal area, if possible with a hard surface.
Engine oil
Visual control of leaks
With an oily engine and high oil consumption, check the areas most likely to develop leaks:
- Open the filler cap and check the seal for cracks or damage;
- Crankcase ventilation: For example, vent hose from cylinder head cover to air intake hose;
- Cylinder head cover gasket;
- Cylinder head gasket;
- drain plug (sealing ring);
- Oil filter gasket: filter joint with flange;
- Oil pan gasket;
- Front and rear crankshaft seals.
Since in the presence of leaks, the oil spreads over a large surface of the engine, it is difficult to immediately determine the location of leaks. To detect leaks, proceed as follows:
1. Wrap the generator in polyethylene.
2. Spray the engine with a normal cold cleaner and after a short time wash it with water at a car wash.
3. Sprinkle the joints of engine components on the outside with lime or talc.
4. Check the oil level, top up if necessary.
5. Test drive for about 30 km on the highway, as the oil in a hot engine reduces its viscosity and leaks out faster at leaks.
6. Finally, examine the engine with a lamp and locate leaks by troubleshooting.
Level check
Check the oil level approximately every 1,000 km and top up if necessary. For 1000 km, the car should consume no more than 1.0 liters of oil. Higher flow indicates worn seals and/or piston rings or seals.
Checking the engine oil level is an important preventative engine maintenance procedure. A constantly low level indicates the presence of oil leaks as a result of failed oil seals, damaged seals, worn piston rings or valve guides. If the oil resembles milk in color or consistency, or there are drops of water in it, this indicates a possible damage to the cylinder head gasket, or the formation of cracks in the body of the head (OK) or block. The check must be made without delay. When measuring the oil level, always also check its condition. Using your thumb and forefinger, remove traces of oil from the dipstick blade - if there are small metal particles in it, the oil must be replaced (see Section Changing the engine oil and oil filter).
1. Park the car on level ground.
2. Park the car on level ground.
3. Warm up the engine to operating temperature and turn it off. Wait 3 minutes for the oil to drain into the oil pan.
4. Remove the dipstick for measuring the oil level and wipe it with a clean cloth.
5. Then insert the dipstick as far as it will go and remove it again. The oil level must be between the MIN and MAX marks
6. Add oil if its level lies near the lower mark.
Engine oil dipstick (1) with marks and probe guide (2)
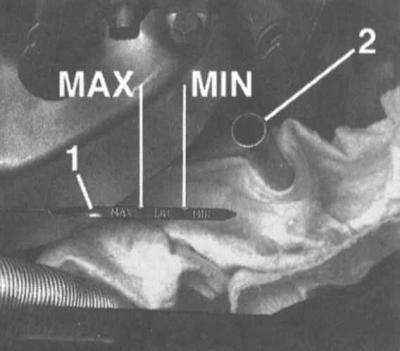
The volume of oil corresponding to the difference between the marks «MIN» And «MAX» corresponds to 1.0 l.
Engine coolant
Do not allow antifreeze to come into contact with exposed areas of the body and painted surfaces of the car. Wash off accidental splashes with plenty of water without delay. Remember that antifreeze is a highly toxic liquid and getting it into the body, even in small quantities, is fraught with the most serious consequences, even death. Never leave antifreeze stored in a loosely closed container, immediately collect spilled coolant on the floor. Remember that the sweet smell of antifreeze can attract the attention of children and animals. Consult with local authorities about ways to dispose of used coolant - in many regions of the world there are special points for receiving various kinds of waste. Never drain old coolant down the drain and onto the ground!
Recently, non-toxic grades of antifreeze have been developed, however, they must also be disposed of in an organized manner.
All models of vehicles described in this manual are equipped with an overpressure compensation type cooling system. The expansion tank of the cooling system made of translucent plastic is located in front of the bulkhead of the engine compartment. When the engine warms up, the coolant (coolant) expands, and its excess flows through a valve mounted in the radiator filler cap into the expansion tank. As it cools, the liquid returns through the hose back to the radiator, which allows you to constantly maintain its normal level in the system.
Do not remove the cap from the filler neck of the radiator/expansion tank when the engine is hot!
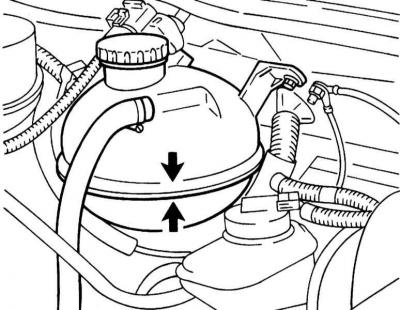
The coolant level in the expansion tank is checked regularly and should not fall below the KALT/COLD mark on the side of the translucent plastic reservoir when the engine is cold. If necessary, make the appropriate adjustment by adding the required amount of fresh mix to the reservoir.
Checking the coolant level through the translucent walls of the expansion tank
Use only the correct mixture of ethylene glycol and distilled water to correct the fluid level (about 50/50). Remember that the frequent use of plain water for this purpose leads to a gradual dilution of the antifreeze and the loss of frost resistance and anti-corrosion properties of the mixture. You should also not abuse various types of additives.
A constant drop in the coolant level usually indicates the development of leaks in the system. Check the radiator, connecting hoses, filler cap, drain plugs and water pump housing for signs of leakage. If no signs of leaks can be detected, a pressure test of the radiator cap should be carried out in a car service workshop.
If it is necessary to remove the radiator cap, wait for the engine to cool completely, then wrap the neck with a thick layer of rags and slowly unscrew the cap to the first stop. If this produces steam, let the engine cool down a little more, only then remove the cover completely.
In addition to the level, always also check the condition of the coolant - it should be relatively clear. If the coolant is rust reddish brown, the cooling system must be emptied, flushed and filled with a fresh mixture of antifreeze and water. Even if the fluid does not change externally, the corrosion inhibitors it contains will wear out over time, so the coolant must be changed regularly in accordance with the vehicle's routine maintenance schedule (see Section Schedule of ongoing maintenance).
Try not to allow antifreeze to come into contact with exposed skin or painted surfaces of body components. Accidental splashes should be washed off immediately with plenty of water.
Washer fluid for windows and headlight lenses
The fluid for washing the windshield and rear windows is poured into a special reservoir made of plastic, located in the left corner of the engine compartment between the shock absorber and the bulkhead; The headlamp washer fluid reservoir is located in front of the shock absorber strut. In temperate regions, clean water can be used as windshield washer fluid, but do not fill the reservoir more than 2/3 to compensate for the expansion of water when it freezes during frost. When operating the vehicle in harsh environments, use only proprietary windshield wipers that provide an adequate drop in the fluid's freezing point. To avoid freezing of the glass when washing in cold weather, preheat it by blowing air passed through the heater heat exchanger.
Windshield washer fluid reservoir
Headlight washer fluid reservoir
Mixing rules are usually printed on the container label. Do not use antifreeze used in the cooling system to add to the washer fluid - the latter is aggressive towards the paintwork of body panels!
Battery electrolyte
The vehicles covered in this manual are equipped with a maintenance-free, sealed-type battery with only vent holes in the casing. The battery case can be made of translucent plastic - in this case, the electrolyte level in its banks can be monitored in order to obtain indirect information about the correct functioning of the charge system and the current state of the battery. If during the operation of the vehicle the battery was replaced for any reason with a conventional (serviced type), you should check the electrolyte level in its banks from time to time, for which it is necessary to remove the upper control / filler plugs. Particular attention should be paid to the electrolyte level in the warm season. Only distilled water should be used to correct the electrolyte level.
Brake and clutch fluid
The brake fluid reservoir is divided into two chambers, each for its own braking circuit. The screw cap has a vent that must always be open. The transparent walls of the tank make it easy to determine the level of the brake fluid.
Master brake cylinder (GTZ) mounted on the servo block of the vacuum brake booster. The tank mounted on top of the GTZ is used as a backup in the hydraulic paths of the drive of both the brake mechanisms and the clutch (see chapters Clutch and drive shafts and Brake system).
The fluid level inside the GTZ tanks and the clutch drive is clearly visible through the translucent walls of the latter and must be maintained between the MIN and MAX marks.
The liquid level in the GTZ tank is clearly visible through its translucent walls

If the fluid level needs to be adjusted, carefully wipe the cap of the respective reservoir and the area around it with a clean cloth to prevent dirt from entering the hydraulic system.
When pouring liquid into the tank, make sure that it does not splash onto the surrounding painted surfaces of the body elements. Add only the specified grade of fluid to each system - mixing two fluids of a different grade is unacceptable and may lead to failure of the corresponding system!
Brake fluid is highly chemically aggressive - do not let it get into your eyes and onto painted surfaces of body panels! Do not use to add to the system a working fluid that has stood for more than one year, or has been stored in a loosely closed container. Remember that brake fluid is very hygroscopic, ie. has the ability to absorb moisture from the air, as a result of which the effectiveness of the brake system can be dangerously reduced!
During the level adjustment step, you should also carefully check the condition of the liquid and the internal walls of the tank. In case of dirt deposits, solid foreign particles or water droplets, the system must be emptied and filled with fresh brake fluid (see chapters Clutch and drive shafts and Brake system).
Once the reservoir is filled to the required level, place the lid firmly on it.
Remember that the level of the working fluid in the GTZ reservoir gradually drops as the friction linings of the brake pads actuate, but this decrease is always very small. If the fluid has to be topped up too often, therefore, there is a leak in the system, the source of which must be identified without delay, and the cause eliminated - carefully inspect all brake lines and their union connections, including calipers, wheel cylinders and vacuum booster servo (see Section Checking the brake system). A drop in the fluid level in the clutch hydraulic reservoir indicates the development of leaks in the tract, including the slave cylinder (see chapter Clutch and drive shafts).
If, during a check of the fluid level in the master cylinders, the fact that its reservoir is almost empty is revealed, the corresponding system must be completely bled (see chapter Clutch and drive shafts or Brake system).
Power steering fluid
The power steering fluid reservoir is located in the front of the engine compartment, behind the left headlight.
The tank lid is equipped with a built-in measuring probe. The verification procedure is standard for all measurements with probes.
Checking the level of the working fluid in the power steering reservoir
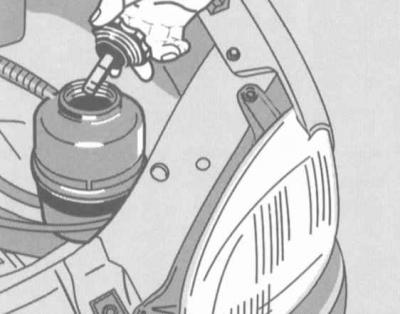
Try not to allow the liquid level to go beyond the lower limit of the allowable range.
If necessary, make an appropriate level adjustment by adding the power steering fluid of the required grade to the reservoir neck.
If the need to adjust the fluid level occurs regularly and frequently, check for signs of leakage of the steering pump, rack and pinion housing, as well as all connecting lines of the hydraulic path of the system and their union connections.
Gearbox oil
The transmission oil does not need to be changed. The oil level must be corrected if a leak is found in the power unit or after installing a manual transmission. When filling the manual transmission with oil, it may leak from the control hole. Place a suitable container under the manual transmission to collect the oil.
1. Drive the car onto a flyover or inspection hole, or jack it up and place it on supports in a strictly horizontal position. Checking the transmission oil level should be done before the trip, or at least 5 minutes after the engine is stopped - the oil should have time to drain into the manual transmission oil pan.
2. Thoroughly wipe the surface of the box crankcase around the control plug. The plug is located on the left rear of the manual transmission.
The location of the control hole plug on the manual transmission

On the 1.6 liter engine, the plug is located on the left front of the manual transmission.
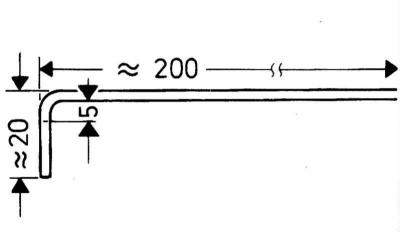
3. Make a hook in accordance with the accompanying illustration and insert it into the hole - the oil level must be at least 2 cm from the lower edge of the control hole.
Dipstick for checking the level of transmission oil in manual transmission
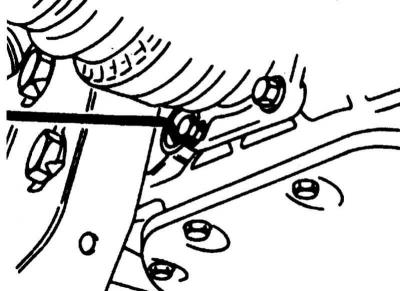
4. The oil level is adjusted through the hole for installing D / V reversing lights, or through a special filler hole - unscrew the sensor / plug.
The location of the filler hole on the manual transmission
5. Continue to add oil until it starts to flow over the edge of the control hole, allow the excess to drain, then plug the control hole with a plug and tighten the latter with the required force.
Do not add too much oil at once. The oil has a certain viscosity and it takes some time for it to flow down.
6. Replace the sensor switch or filler plug and tighten it/her to the required torque.
ATF
Maintain cleanliness when carrying out the procedures described below.
Correct ATF level is one of the critical performance parameters for AT equipped models. An excessive drop in the ATF level can cause the rotation converter to slip, while an excessive amount of fluid leads to its foaming, leakage and is fraught with transmission failure.
Checking the ATF level should be done with the transmission warmed up to normal operating temperature (15÷20 km run, 72÷80 deg.).
Do not check the ATF level immediately after driving the vehicle at high speeds, in urban conditions in hot weather, or after towing a trailer - let the fluid cool down for about 30 minutes beforehand!
1. Park the vehicle on a level, hard paved area and apply the parking brake firmly. If the engine is cold, start it and warm it up to normal operating temperature at idle. With the engine running, depress the brake pedal and alternately move the AT selector lever through all positions, finally returning it to the position «R».
2. Without turning off the engine so that the torque converter is filled with transmission fluid, remove the dipstick from the guide tube. Using your fingers, remove traces of ATF from the dipstick blade and evaluate its condition by touch. The check can be made both on a cooled down and on a warm engine. Since the ATF level depends on engine temperature, the dipstick has two scales. The scale on one side is designed to check the ATF level at a temperature of 80 degrees, and on the other side - at a temperature of 20 degrees.
The ATF dipstick is placed in the space between the battery and the engine
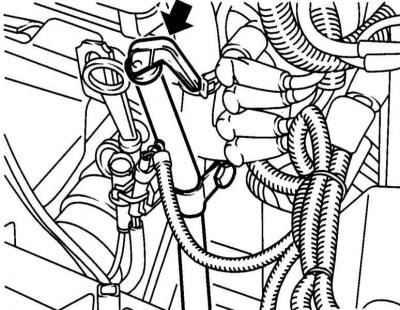
3. When cooled down AT (ambient temperature below 35 degrees.) The test must be completed one minute after the engine starts. Wipe the blade thoroughly with a clean rag and insert the probe back into the guide tube, seating the cap firmly on the mouth.
4. Remove the dipstick from the throat again and determine the ATF level in the transmission housing by the length of the wetted area of the blade. If necessary, make the appropriate adjustment by adding the required grade of transmission fluid through a funnel - pour ATF directly into the neck of the dipstick guide tube.
MIN and MAX marks on the probe blade
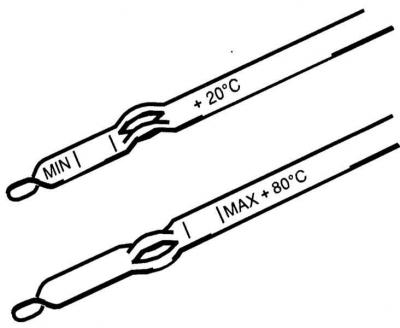
Difference between marks «MIN» And «MAX» on «cold» side of the dipstick corresponds to 0.35 l, and on «hot» side - 0.2 l.
Add ATF in small portions in several steps, each time checking the level. Do not overfill the oil, as its excess can lead to problems in the work of AT. Excess oil must be drained or pumped out. Press the brake pedal and slowly move the selector lever to all positions in sequence. After that, check the ATF level again.
All approved ATFs can be mixed with each other. Do not use any additives.
At the same time as the level, the condition of the ATF should also be checked. If the fluid wetting the tip of the dipstick blade is dark red-brown or smells of burning, the ATF should be replaced (see chapter Automatic 4-speed transmission). If you are unsure about the correct assessment of the condition of the transmission fluid, compare it by color and smell with fresh ATF.
Do not start the engine and do not tow the car without ATF in the torque converter and AT.

Visitor comments