MulTec central injection system
The components included in the MulTec system are listed in the accompanying illustration. In terms of the efficiency of functioning, the system meets all the requirements of international standards.
Main components and functional diagram of the MulTec injection system (engine OHC 1.2 l)
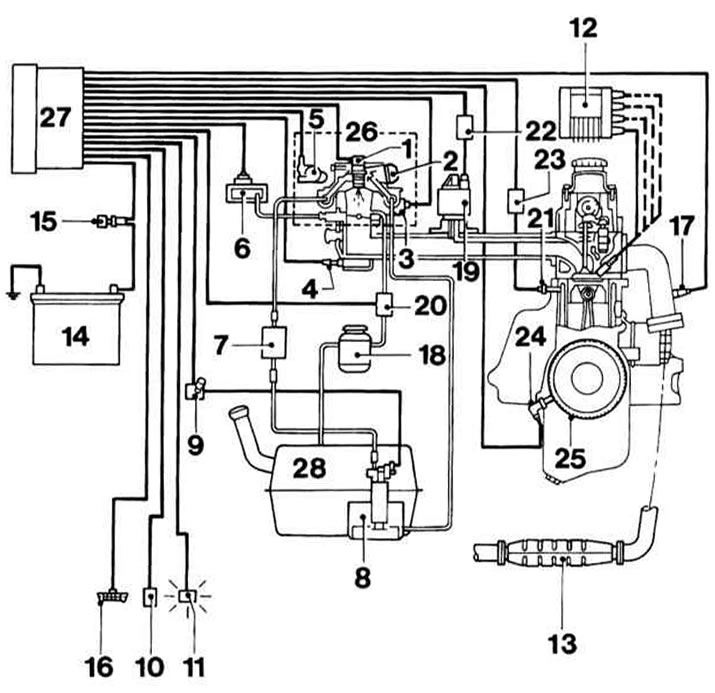
1 - Injector
2 - Fuel pressure regulator
3 - Step e / motor of the idle speed stabilization system
4 - Intake air temperature sensor (IAT)
5 - Throttle valve potentiometer (TPS)
6 - Pressure sensor in the intake manifold (MAP)
7 - Fuel filter
8 - Fuel pump
9 - Fuel pump relay
10 - Frequency mileage sensor
11 - Control lamp failures (MIL)
12 - DIS ignition module
13 - Catalytic converter
14 - Battery
15 - Ignition lock
16 - Diagnostic connector
17 - Lambda probe
18 - EVAP fuel vapor adsorber
19 - EGR valve
20 — the Control valve of system EVAP
21 - Knock sensor (KS)
22 - EGR control unit
23 - Detonation adjustment unit
24 - CKP sensor
25 - Crankshaft gear with CKP sensor rotor
26 - Throttle body
27 - Engine control unit (ECM)
28 - Fuel tank
The fuel pump delivers fuel from the tank through the fuel filter to the throttle body or fuel rail.
The air-fuel mixture is injected into the throttle body through a central injector and enters the intake manifold, from where it is distributed to individual cylinders. The pressure regulator maintains the pressure in the intake manifold at the level 0.76 atm.
MulTec-M
4 injectors are connected to the fuel line. The pressure regulator maintains fuel pressure in the line equal to 3.0 atm. The injectors are electronically controlled and inject fuel simultaneously into the intake manifold ahead of the intake valves.
Air is sucked in by the engine through the air filter and the throttle valve, through which the required amount of fuel is regulated. The vacuum in the intake manifold is registered by the corresponding sensor, as well as the temperature of the intake air. From these parameters, the control module determines the mass of intake air. The intake air pressure sensor is located on the bulkhead of the engine compartment and is connected via a vacuum hose to the intake manifold.
The ECM regulates the amount of fuel to be injected according to the intake air mass and other parameters such as engine temperature.
MulTec-S
From the fuel distribution line, fuel flows to the injectors. The pressure regulator in the line ensures that the pressure in it is maintained equal 3.0 atm. The injectors are controlled separately. The injection is made in accordance with the ignition sequence, at the right time.
On engine 1.6 l 109 hp the intake air mass is recorded by the MAF sensor. On other engines, the mass of intake air is determined by the magnitude of the vacuum in the intake manifold. Determination by mass is more accurate and faster. The ECM regulates the amount of fuel injected according to the measured air mass and other parameters such as engine temperature.
Bosch Motronic 1.5.5 injection system
The accompanying illustrations components of the injection system for DOHC 1.0 and 1.2 l engines are presented.
Components of the Bosch Motronic injection system (DOHC 1.0 and 1.2L engines)
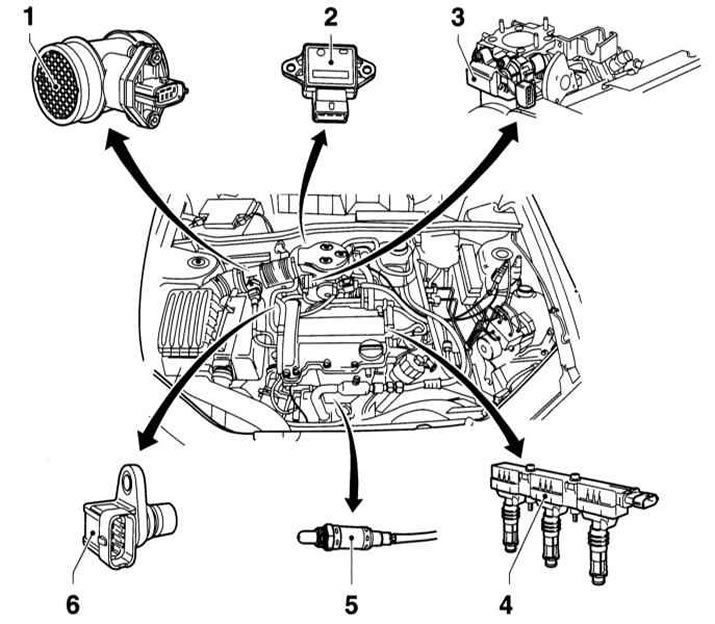
1 - MAF sensor
With the definition of reverse flow, i.e. when calculating the amount of injected fuel, the volume of air discarded when the intake valves are closed is taken into account. This provides more accurate fuel delivery.
Additionally, an intake air temperature sensor is integrated into the body of the air mass meter
2 — TPS
Sends information to the ECM about the current throttle position.
3 - Stepping e / motor throttle
Based on the signals from the ECM, the stepper motor sets the throttle position and thus the idle speed
4 - Ignition module
The ignition module is put on the spark plugs and fixed to the cylinder head cover. Each spark plug has its own ignition coil, which is located directly above the built-in spark plug connector. BB wire missing
5 - Lambda probe
6 - CMP sensor
Components of the Bosch Motronic injection system (DOHC 1.0 and 1.2L engines)
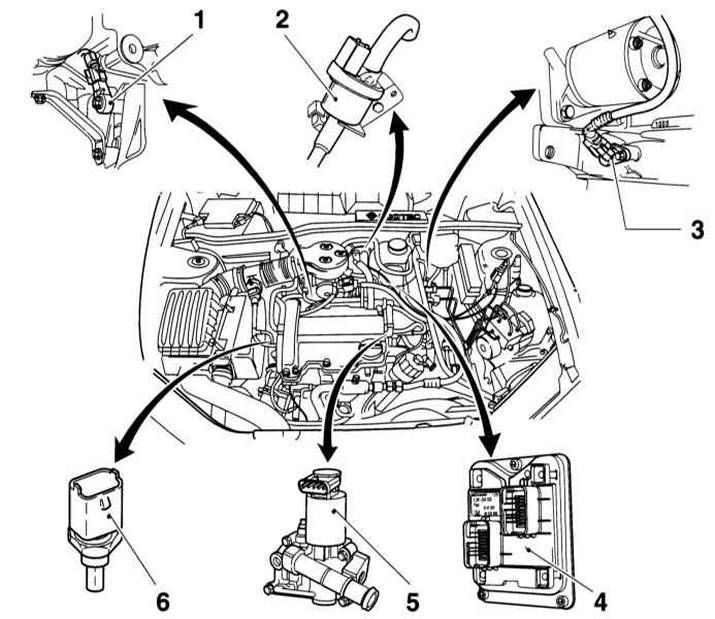
1 - Knock sensor
2 — the Valve of management of a purge of an adsorber of the EVAP system
3 - CKP sensor
4 - Engine control device
It is located directly at the engine or at the inlet pipeline. This ensures the minimum cable length. Has 2 connectors: for engine and instrument cluster
5 - EGR valve
Located in the EGR housing and controlled by the ECM, it regulates the amount of exhaust gases returned to the engine. The EGR housing is attached to the cylinder head and connects the exhaust manifold through a channel in the cylinder head to the intake manifold. The EGR housing has a coolant passage leading to the heater.
Next to the EGR valve is an ECT sensor that sends a signal to a pointer located on the instrument cluster
6 - ECT sensor
Sends coolant temperature data to ECM
Elements of the injection system (all engines)
The TPS is located directly on the throttle shaft. It sends information to the ECM about the current throttle position.
The fuel pump relay is located in the footwell, behind the right A-pillar cover. The ECM is also located there. The relay controls the power supply to the fuel pump and cuts off power as soon as the ignition pulses stop, for example, if the engine stalls.
The CKP sensor is located on the side of the engine compartment. It transmits information about the number of revolutions of the crankshaft to the ECM.
The lambda probe measures the oxygen concentration in the exhaust stream and transmits the corresponding signals to the ECM. Based on the information received, the ECM changes the quality of the air-fuel mixture, which ensures optimal afterburning of exhaust gases in the catalytic converter.
The stepper motor of the idle speed stabilization system regulates the idle speed, maintaining it unchanged, regardless of the use of additional units, such as power steering or K / V. The motor is controlled by the ICM.
The EVAP control valve is located on the bulkhead of the engine compartment. When the valve is open, fuel vapors from the canister are sucked in and burned in the engine.
The adsorber accumulates fuel vapors that are formed in the fuel tank due to temperature changes. The accumulated fuel vapors are then used and do not enter the atmosphere.
The presence of knock control provides on the engine 1.2 l and engines DOHC 1.4 and 1.6 L the possibility of working at the detonation boundary and adaptation to the quality of the fuel used. Knock control allows the engine to run at a high compression ratio. This, in turn, provides the possibility of optimal use of fuel energy, which leads to a reduction in fuel consumption.
MAF sensor on engines 1.6 l (109 hp) located at the outlet of the air filter. The MAF sensor housing contains a thin glowing film that is cooled by the flow of air around it. The control system regulates the heating current so that the temperature of the film (resistance controlled) remained constant. If, for example, more air is sucked in as a result of an increase in the throttle opening angle, the plate cools down. As a consequence, the value of the heating current increases so that the temperature remains constant. The value of the current in this case corresponds to the mass of the sucked air.
CKP sensor in the system MULTEC-S serves to define the cylinder for sequential injection. With this sensor, the ECM determines, for example, when the piston of cylinder 1 is at TDC.
On engines DOHC 1.4 and 1.6 l from 09.1994 release the system of admixture of additional air corrects the composition of the exhaust gases when the engine warms up.

Visitor comments