The crankshaft is held in five bearings, the center bearing has flanges to adjust the side play.
The connecting rods are connected to the crankshaft by bearings, and to the pistons by piston pins, which are fixedly seated in the upper head of the connecting rod. Aluminum pistons - contain three piston rings: two compression rings and a third - an oil scraper ring.
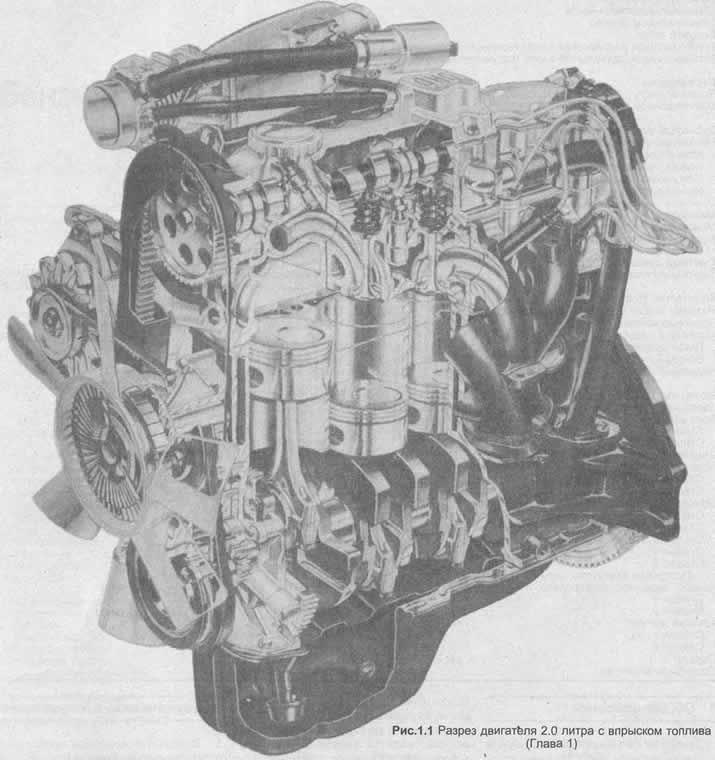
The camshaft is driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft, and controls the valves through rocker arms. The ends of the rocker arms rest on hydraulic self-adjusting valve lifters which automatically eliminate any gap between the rocker arm and the valve stem. The intake and exhaust valves are closed by a single spring and move in guides that are pressed into the cylinder head.
Engine lubrication is carried out by a pump located in a casing attached to the front end of the cylinder block. The oil pump is driven by the crankshaft, while the distributor runner and, on carburetor models, the fuel pump are driven by the camshaft. Crankcase gases are fed into the camshaft housing through a pipe and then enter the intake manifold.

Visitor comments