Light and signal equipment
Check all warning lights and vehicle lighting. Replace burnt out light bulbs. Check the operation of the horn.
Checking the wear of the brake linings and brake discs
Front brakes
1. Remove the front wheels.
2. To check the condition of the brake linings, caliper and brake disc, the brake linings must be removed. The approximate thickness of the brake pads can be checked through the hole in the caliper.
3. If any brake lining is less than the minimum thickness, all four brake linings on both wheels must be replaced.
Rear brakes
1. Remove rear wheels.
2. To check the condition of the brake linings, caliper and brake disc, the brake linings must be removed. The approximate thickness of the brake pads can be checked through the hole in the caliper.
3. If any brake lining is less than the minimum thickness, all four brake linings on both wheels must be replaced.
Drive belt
Examination
The drive belt must be regularly inspected along its entire length and if it is worn or damaged, it must be replaced.
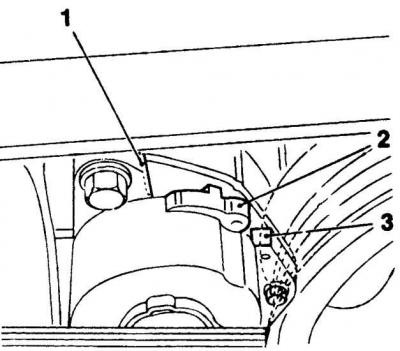
1. On the 2.0L engine, check that the tensioner lever pointer (2) was located between the abutments (1 and 3). Replace the belt if it is worn or the tensioner arm touches the stop.
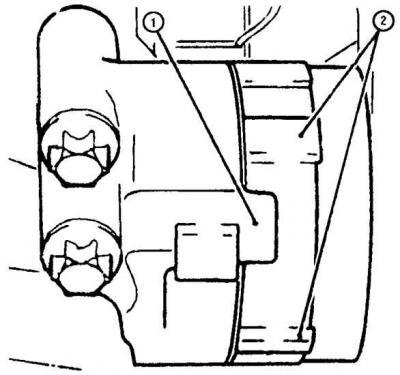
2. On 2.5L and 3.0L engines, check that the stop (1) was between the ledges (2) on the lever. Replace the belt if it is worn or the tensioner arm touches the stop.
Replacement
2.0L engine
1. Move the tensioner pulley aside by putting the wrench on the pulley center bolt and remove the belt. Lock the tensioner in this position and put on a new belt. Release tensioner.
2.5L and 3.0L engines
2. Remove the airbox and front air intake pipe.
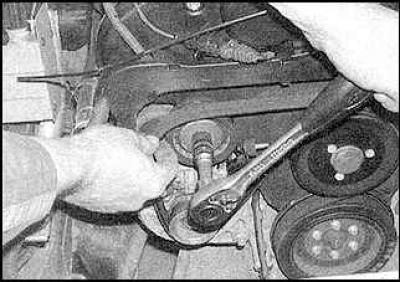
3. Move the tensioner pulley aside by putting the wrench on the pulley center bolt and remove the belt. Put on a new belt and release the tensioner.
Hoses and connections - checking for leaks
Cooling system
1. Check the radiator and heater hoses along their entire length. Replace worn hoses. Check the reliability of the clamps and the condition of the hoses under them.
2. Inspect all components of the cooling system for leaks. A leak in the cooling system is indicated by white or rusty deposits in the area of the leak. Replace related elements or gaskets if necessary.
Supply system
1. Raise the vehicle and inspect the fuel tank and filler hose for punctures, cracks, or other damage. Check connections.
2. Check all rubber hoses and metal pipes coming from the fuel tank. Check the reliability of connections and fastenings.
Engine oil
Inspect the area around the valve cover, cylinder head, oil filter and oil sump for leaks. Replace appropriate gaskets or seals.
Automatic transmission fluid
Inspect the automatic transmission coolant hoses for damage or leaks.
Power Steering System
1. Check the condition of the hoses connecting the hydraulic fluid reservoir, pump and steering gear.
2. Check connections and tightness of clamps.
Air conditioning refrigerant
The air conditioning system is filled with pressurized liquid refrigerant. If a leak is found in the air conditioning system, contact a specialist immediately.
Brake fluid
1. Inspect the area around the brake pipe connections on the brake master cylinder and the base of the brake fluid reservoir for leaks. Check the pipe connections on the ABS hydraulic module.
2. Check the brake calipers and brake pipes under the vehicle.
Manual transmission oil
Inspect the area around the driveshaft oil seal at the rear of the transmission for signs of leakage. Check the oil level and replace the seal if necessary.
Final drive fluid
Inspect the area around the seals and seals of the driveshaft and axle shafts for leakage. Check the oil level and replace the seals if necessary.
Determining the source of the leak and the type of fluid
If the source of the leak and the type of fluid are difficult to determine immediately, leave the vehicle overnight and place a piece of clean cardboard under the suspected leak. In the morning, even a small leak will be noticeable.
Vacuum hoses
Under the influence of high temperatures inside the engine compartment, rubber and plastic hoses gradually harden and destroy, which ensure the operation of various engine components and the exhaust gas toxicity reduction system. You should periodically check the condition of the hoses, the presence of cracks and hardening, loose connections, leaks.
Part of the hoses are attached with clamps. Check the tightness of the clamps, as loosening the fastening leads to a leak. In those places where clamps are not provided, check the reliability of the hose seal on the fittings, loss of elasticity in such connections due to swelling or hardening of the hoses is not allowed, otherwise the tightness of the connection is violated.
Vacuum hoses can be distinguished by their color or by the colored strips glued to them. Vacuum hoses with different wall thicknesses, atmospheric compression resistance and heat resistance are used for different engine systems. When replacing, make sure that the new vacuum hoses exactly match the ones being replaced.
Often the hose can only be checked after it has been removed from the vehicle. If several hoses are being removed, first mark the mating fittings and hoses so as not to disturb their relative position later.
When checking the condition of the vacuum hoses, at the same time inspect the plastic tees. Check for cracks on them, as well as deformation of the hose at the point of contact with the tee fitting, which may be the cause of a leak.
To check for leaks by a characteristic sound, you can use a piece of vacuum hose with an internal diameter of about 6.0 mm. Having attached the end of the hose to the place to be checked, listen through the opposite hole in the hose. characteristic "hiss" indicates a leak.
Fuel hoses
Check the rubber fuel hoses for signs of wear or deterioration. Check hoses especially carefully at kinks and near connections, such as the connection to the fuel filter.
When replacing the fuel line on injection engines, the new line must exactly match the one used in the fuel system of engines of this type.
To fasten the fuel line hoses, spring clamps are usually used, which lose their elasticity over time. When disassembling the connection, such a clamp must be unbent, after which the elasticity is completely lost. Always replace spring clamps with screw clamps when replacing hoses.
Metal tubes
Metal pipes are commonly used in the fuel line to connect the fuel pump to the fuel pressure regulator on the injector rail. Check for deformed tubes (twisted) areas and small incipient cracks.
When replacing, only seamless steel tubes should be installed. Tubes made of copper or aluminum are not suitable, as they cannot withstand vibration loads from the engine.
Check the condition of the metal pipes and fittings of the hydraulic brake system at the junction with the main brake cylinder and dispenser (if provided), cracks and loose connections are not allowed. If any signs of brake fluid leakage are found, immediately carefully check the entire circuit of the brake hydraulic system.
Body anti-corrosion coating
To check the anti-corrosion coating of the bottom and body, you must contact the experts.
Hand brake - check and adjustment
1. Raise the rear of the vehicle and place it on stands.
2. Raise the handbrake lever 6 clicks and check that both rear wheels are locked.
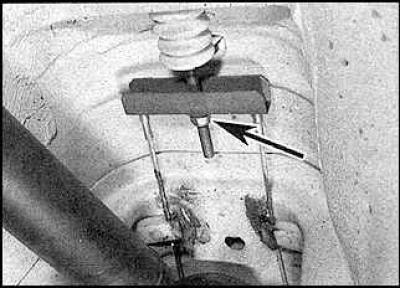
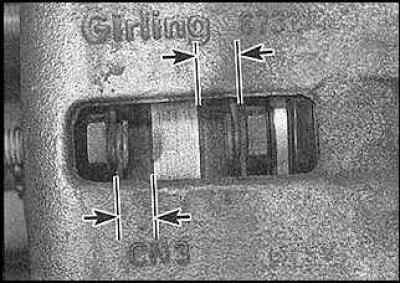
3. If adjustment is necessary, raise the handbrake lever 3 clicks and loosen the adjusting nut on the balancer (arrow).

4. Rotate the brake disc so that the hole in the disc is positioned over the adjusting nut on the brake shield. With a screwdriver inserted into the hole, turn the adjusting nut until the brake pads block the brake disc. Then loosen the nut just enough so that the brake disc can turn again. Perform the same operation on the second wheel.
5. Tighten the adjusting nut on the balancer so that the pads begin to block the brake disc.
6. Check handbrake adjustment.
Checking the front suspension and steering
1. Raise the front of the car and place it on stands.
2. Inspect the boots and boots for cracks or signs of wear.
3. On models with a power steering system, inspect the system hoses and pipes and their connections for leaks.

4. Grab the wheel from above and below and try to shake it. If the free play is too great, ask an assistant to depress the brake pedal and shake the wheel again. If the free play has decreased or disappeared, then the hub bearings must be replaced. If there is still free play, then the connections or suspension mounts are worn out.
5. Grab the side of the wheel and try to shake it. Too much free play can be caused by worn hub bearings or tie rod ball joints.
6. Check up a condition of plugs of fastenings of elements of a suspension bracket.
7. Lower the vehicle to the ground and turn the steering wheel 1/8 turn to either side. If the steering wheel play is too great, check the steering gear joints and connections.
Checking the rear suspension
1. Raise the rear of the vehicle and place it on stands.
2. Check the hub bearings, bushings and rear suspension mountings as described higher for the front suspension.
Checking shock absorbers
1. Inspect shock absorbers for signs of fluid leakage. If a leak is present, the shock absorber must be replaced.
2. Test the effectiveness of the shock absorbers by rocking the car up and down.
Wheel bolt tightening torques
1. Loosen the fixing bolts and clean the threads of the bolts.
2. Tighten the bolts to the required tightening torque.
Adjustment of headlights and sidelights
To accurately adjust the headlights, you need to contact a specialist. If necessary, adjusting screws can be used.
All models have an electric drive for adjusting the headlights depending on the load of the car. The switch must be set to the following position depending on the vehicle load:
| 0 | Front seats occupied |
| 1 | All seats are occupied |
| 2 | All seats are occupied and cargo is in the luggage compartment |
| 3 | Occupied driver's seat and cargo in the luggage compartment |
Checking the car on the road
Instruments and electrical equipment
1. Check the operation of all appliances and electrical equipment.
2. Check the accuracy of the sensors. Turn on all the elements of electrical equipment in turn to check their operation.
Steering and suspension
Check the operation of the steering and suspension. Check that there is no vibration or noise when driving.
Transmission
Check the operation of the engine, clutch, gearbox and axle shafts. Check that they do not make any unusual noise when moving.
Checking the brake system
1. Check that the car does not pull to the side when braking and that the wheels do not lock up too early.
2. Check that the steering wheel does not shake when braking.
3. Check the operation of the hand brake and power brake booster. To do this, depress the brake pedal several times and start the engine. The pedal should go down a little. Let the engine run for a few minutes and shut it down. Press the brake pedal. You should hear the vacuum booster hiss. After a few clicks, it should stop, and the pedal should become much stiffer.
Wheel adjustment
Proper wheel alignment is very important for good vehicle handling and tire life.
To check the angle of longitudinal inclination of the kingpin, camber and the angle of the transverse inclination of the kingpin, it is recommended to contact specialists.
Exhaust system
1. Install the car on a viewing hole, overpass or lift it and install it on supports.
2. Inspect exhaust pipes along their entire length for damaged or missing fasteners, check mounting clamps and pipes for rust.
3. Check pipes for leaks and repair if necessary.

Visitor comments