Relationship of individual nodes
In a running engine, pistons moving up and down in the cylinders suck in air. If you fully depress the gas pedal, then the engine sucks in the maximum mass of air, because. in this case, the throttle valve is fully open. Accordingly, the mass of air is less in the closed or partially open position of the throttle valve. For clean engine operation, fuel must be mixed with the intake air in the exact proportion.
Multec-S: To determine the ratio of fuel and air in a combustible mixture, the pressure in the intake pipe and the temperature of the intake air are used as a comparative value.
Simtec: Mass is used to determine the correct fuel/air ratio (weight) intake air. In this case, the change in the resistance of the heating plate serves as a control unit for information about the intake air mass.
For all systems: this control unit is the source of impulses for opening and closing the injection valves. A long opening time is required if a lot of fuel is needed - and a short opening time is sufficient if the required amount of fuel is small. «injection force» injection valves remains constant. The reduction in the amount of fuel is carried out by reducing «injection time».
Starting a cold engine
To start a cold engine, an enriched, more fuel-saturated combustible mixture is needed, since cold engine oil still provides significant resistance to the engine. The increased frictional resistance is compensated by an enriched combustible mixture. During the start-up phase, some of the injected fuel may also condense on the cold walls of the combustion chambers, so it must be further enriched.
This is taken care of by the cold start program, which is stored in the memory of the control unit. In cold start control - this is a certain number of ignitions - the injection duration is increased by valves. Injection duration is affected by factors such as coolant temperature and engine speed. After a certain engine speed, the amount of fuel injected when starting a cold engine is gradually reduced and adapted according to the standard amount.
Warming up
For some time after starting, the engine needs a more enriched combustible mixture, because. the resistance of cold engine oil still needs to be overcome. For this, there is a so-called «boost after launch». Depending on the temperature, more fuel is supplied for some time. The control unit receives the necessary information about the engine temperature from the coolant temperature sensor.
Idling
With closed throttle (released gas pedal) a small amount of air bypasses the throttle through the bypass port. This air is detected by the intake manifold pressure sensor (Multec-S) or air mass meter (Simtec) and therefore supplements the required amount of fuel with the combustible mixture at idle. However, the idling mixture is slightly richer than the normal air-fuel mixture in order to keep the engine running smoothly and without interruption. When a rich idle air-fuel mixture should follow, the control unit learns from the throttle valve potentiometer. How much air should pass through the bypass (and therefore what is the idle speed), defines the idle speed controller.
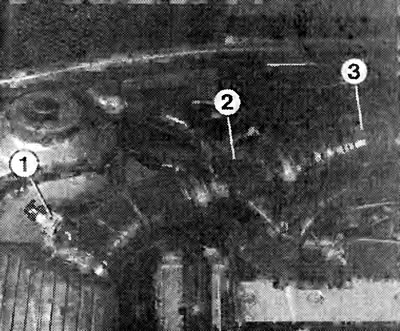
The photo shows a 16V 1.8/2.0L engine with Simtec injection. The numbers indicate:
1 - intake air temperature sensor;
2 - hot-film air mass flow meter;
3 - air intake hose.
Partial load
At partial load, the engine receives a normal amount of fuel. In this case, importance is attached to the lowest possible fuel consumption.
Accelerations
If the accelerator pedal is suddenly pressed, then an enrichment of the air-fuel mixture is caused for acceleration if the increase in the amount or mass of air received per second exceeds a certain value. The throttle potentiometer also provides an acceleration signal. A cold engine requires even more fuel to accelerate. Therefore, the control unit evaluates each impulse of the intake manifold pressure sensor or the air mass meter and the throttle valve potentiometer as an acceleration signal and sends additional fuel.
Full load
The throttle valve potentiometer indicates to the control unit that the driver has fully depressed the gas pedal. In order to develop maximum power, the engine now receives a rich mixture (enrichment of the fuel-air mixture in full load mode).
Forced idle mode
When driving downhill with the gas pedal released, no fuel enters the engine at all. The car itself rolls under the influence of weight or inertia. By high speed and the resistance value of the throttle potentiometer, the control unit knows when the vehicle is in forced idle mode and can «save fuel».
RPM limit
In our Vectra, this is done by the fuel injection system. It compares the current RPM with the maximum RPM and simply closes the fuel valve when this limit is exceeded. This method is necessary in vehicles with a catalytic converter, as in the event of a misfire, unburned fuel would enter the catalytic converter. It harms him.
Anti-Jerk Function
The absence of jerks in the partial load range and during rapid load changes is ensured by an electronic filter in the control unit. It records speed signals over short periods of time and calculates an average value. If required, the approaching jerk is prevented by reversing the ignition timing and suppressed in this effective way.

Visitor comments