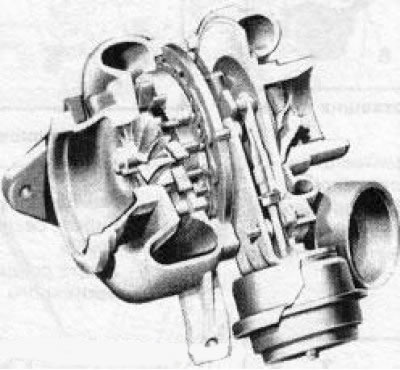
19.2 Turbocharger
2. The turbocharger is a shaft, the central part of which is installed in the bearing. Turbines are located on both sides of the shaft in two separate housings. One of the turbines is included in the exhaust gas duct, the other in the intake tract. When the engine is running, the turbine included in the exhaust tract is set in motion by the exhaust gas flow - while the rotational speed of the turbocharger shaft reaches 300,000 rpm. as a result, the turbine installed at the other end of the shaft creates pressure in the intake tract. Due to the higher degree of filling of the cylinders, the increase in engine power can reach 100%.
3. The air pressure in the intake manifold during turbocharging increases by 0.4-0.8 bar (total pressure reaches 1.8 bar), due to which the engine power is also increased. The air pressure values in the intake air duct are determined by the boost pressure sensor, which transmits the corresponding signal to the electronic module of the engine management system. At the same time, the system controls that the maximum air pressure does not exceed a certain value.
4. Along with the power, the use of a turbocharger also increases the engine torque, which favorably affects the smooth operation of the engine.
5. For optimal engine operation in various modes, a certain amount of air is required. Therefore, for engines and Z19DT (H) /Y22DTRA30DT turbocharger with variable turbine geometry is installed (VNT), i.e. guide vanes are smoothly controlled through the solenoid valve and vacuum chamber. Thus, at any engine speed, the optimum boost pressure is achieved.
6. The turbocharger bearing is lubricated under pressure in the general engine lubrication system. Oil is supplied and discharged to the oil sump through separate pipelines. The bearing housing has hermetic seals.
7. The turbocharger housing is attached to the exhaust manifold. To remove it, it is necessary to disconnect all electrical wiring connectors, fuel and oil lines, remove the exhaust manifold protection and the manifold together with the turbocharger. Then disconnect the turbocharger.
Note: If the cooling system pipes need to be disconnected when removing the exhaust manifold, be sure to drain the coolant.
8. The turbocharger is an assembly made with precision precision. Therefore, it cannot be repaired in a normal car service workshop and is replaced as an assembly.
9. For maximum turbocharging efficiency, there is a charge air cooler between the turbocharger and the engine intake pipe (intercooler). which cools the compressed air. Reducing the intake air temperature leads to an increase in its density, an increase in the filling of the cylinders and the thermal efficiency of the working cycle.
10. The intercooler is mounted on the cooling system radiator assembly, usually in front of it. To remove it, it is necessary to dismantle the front bumper cover and disconnect the air ducts and other supply lines.

Visitor comments